A Wealth of Invaluable Resources
The VRFSC works tirelessly to safeguard people and protect the property of individuals and families living in Ventura County. To this end, we provide the latest resources and tools to learn about wildfires—and to better prepare for the next area wildfire event.
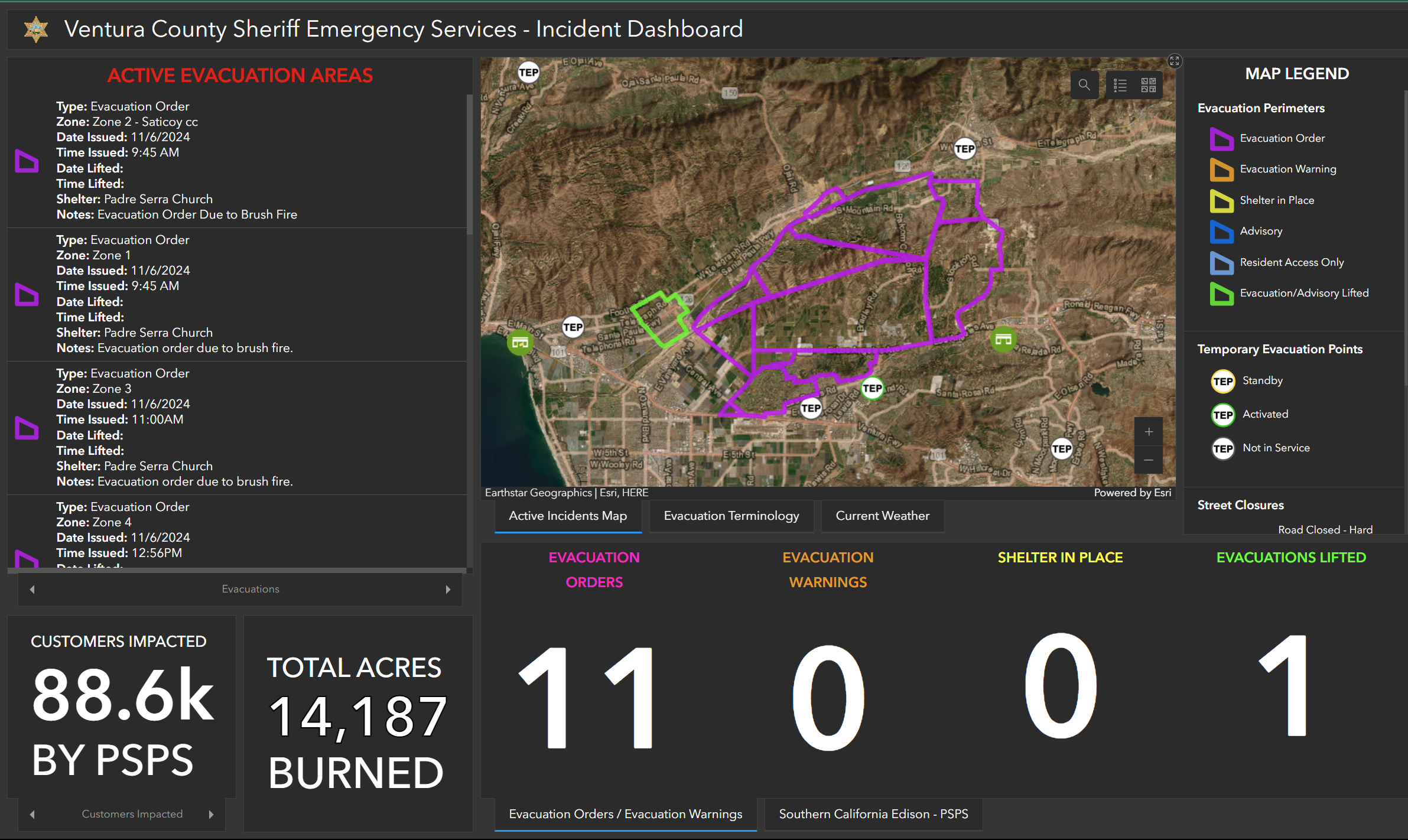
LIVE: ALERTS & INCIDENTS
LATEST: LOS ANGELES FIRES RECOVERY INFO
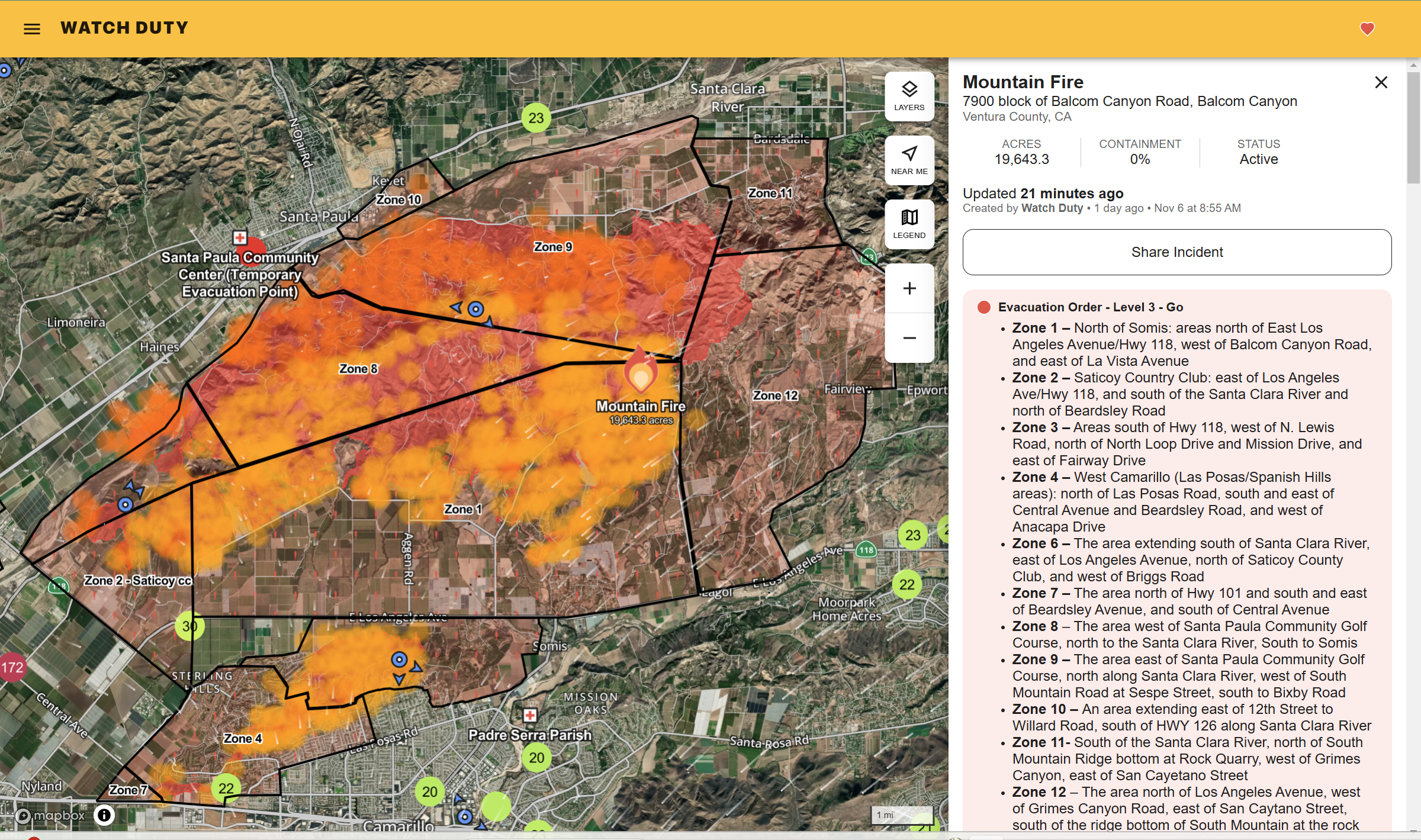
LASTEST: Mountain Fire Information
LIVE MAPS
STAY INFORMED
Safety Tips On Returning Home After A Wildfire
Insurance Claim and Recovery Help
Emergency Preparation
Insurance Claim & Recovery Help
FEMA Assistance is Available for Individuals Affected by the Wildfires in California
As multiple, devastating fires continue to threaten Southern California, FEMA and federal partners are leaning in to support the state-led response. FEMA Administrator Deanne Criswell will be on the ground today to assess damage, speak to survivors and meet with community officials.
On Wednesday, President Biden approved a Major Disaster Declaration to supplement recovery efforts. Los Angeles County residents who have disaster-related needs due to the fires may be eligible for financial assistance. Damage assessments are continuing in other areas, and more counties and additional forms of assistance may be designated after the assessments are completed.
FEMA disaster assistance is intended to meet the basic needs of your household for uninsured or underinsured necessary expenses and serious needs in order to jumpstart your recovery. If you have insurance and are applying for FEMA disaster assistance, you must file a claim with your insurance company first. By law, FEMA cannot duplicate benefits for losses covered by insurance. If insurance does not cover all your damage, you may be eligible for federal assistance.
FEMA Assistance Can Help Jumpstart Recovery
Individuals and families in the designated areas may be eligible to receive money for essential items like food, water, baby formula, breast feeding supplies, medication and other emergency supplies.
Eligible survivors may also receive money to help with housing needs if they cannot return to their home because of the fires. The money can be used to stay in a hotel, with family and friends or other options while they find a more permanent housing solution.
In addition, eligible survivors may receive money for rental assistance, basic home repairs for their primary home, personal property losses and other eligible expenses related to the wildfires.
To learn more about the types of assistance available, visit: fema.gov/assistance/
How to Apply for FEMA Assistance
After making a claim with their insurance provider, the first step residents can take to jumpstart their recovery is to apply for FEMA assistance. There are three ways to apply:
- Online at DisasterAssistance.gov. If you have access to the internet and your electronic devices have power, applying online is the easiest, fastest and most convenient way to apply.
- On the FEMA App for mobile devices.
- Calling the FEMA Helpline at 1-800-621-3362. Calls are accepted every day from 4 a.m. to 10 p.m. Pacific Standard Time. Help is available in most languages. If you use a relay service, such as video relay (VRS), captioned telephone or other service, give FEMA the number for that service. To view an accessible video about how to apply visit: FEMA Accessible: Registering for Individual Assistance - YouTube.
Contact FEMA
If you have any questions, please contact FEMA Office of External Affairs:
- Congressional Affairs at (202) 646-4500 or at FEMA-Congressional-Affairs@
fema.dhs.gov - Intergovernmental Affairs at (202) 646-3444 or at FEMA-IGA@fema.dhs.gov
- Tribal Affairs at (202) 646-3444 or at FEMA-Tribal@fema.dhs.gov
- Private Sector Engagement at (202) 646-3444 or at FEMA-private-sector@fema.
dhs.gov
CA Department of Insurance
United Policyholders
Keep Your Home Protected When Insurance is Limited and Expensive